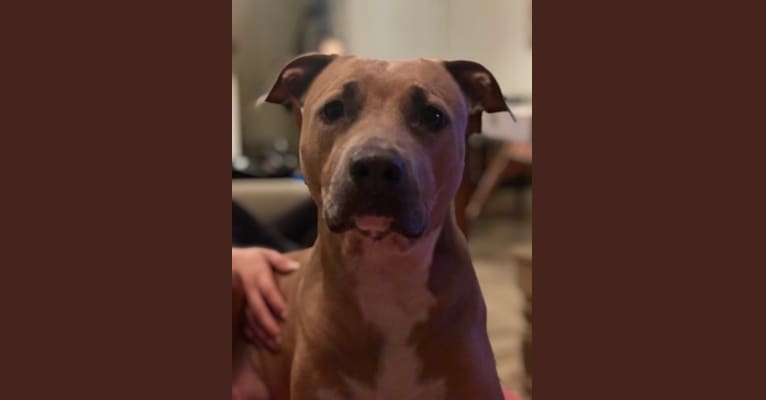
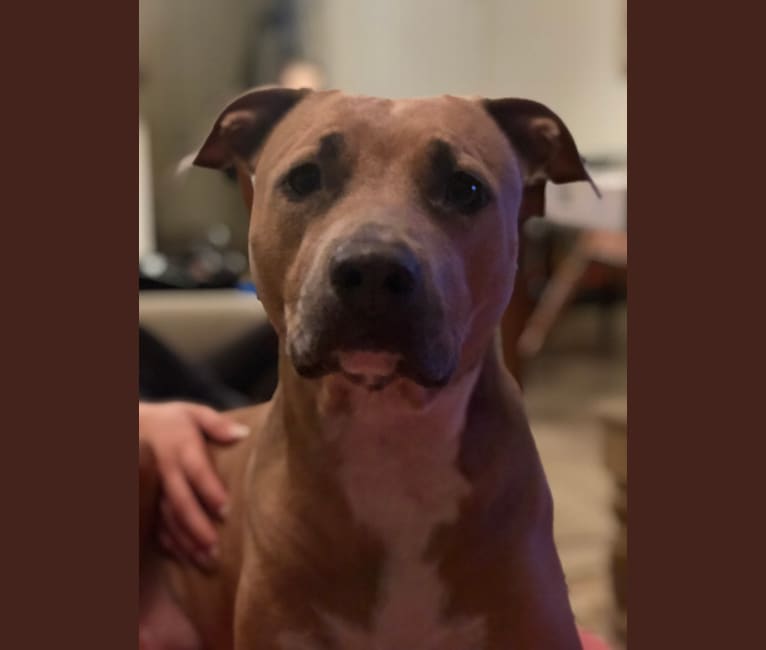
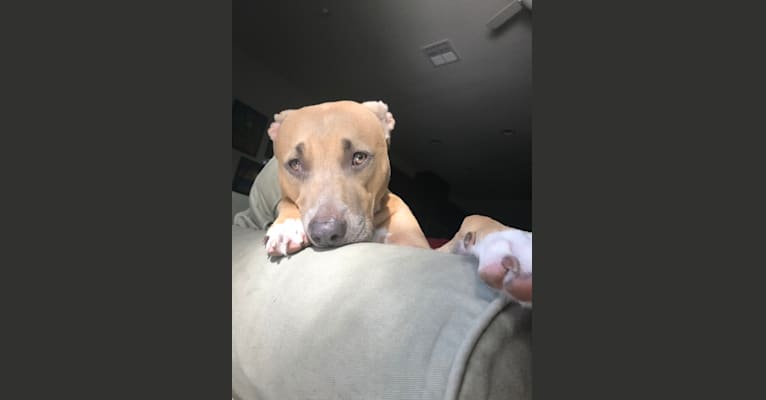
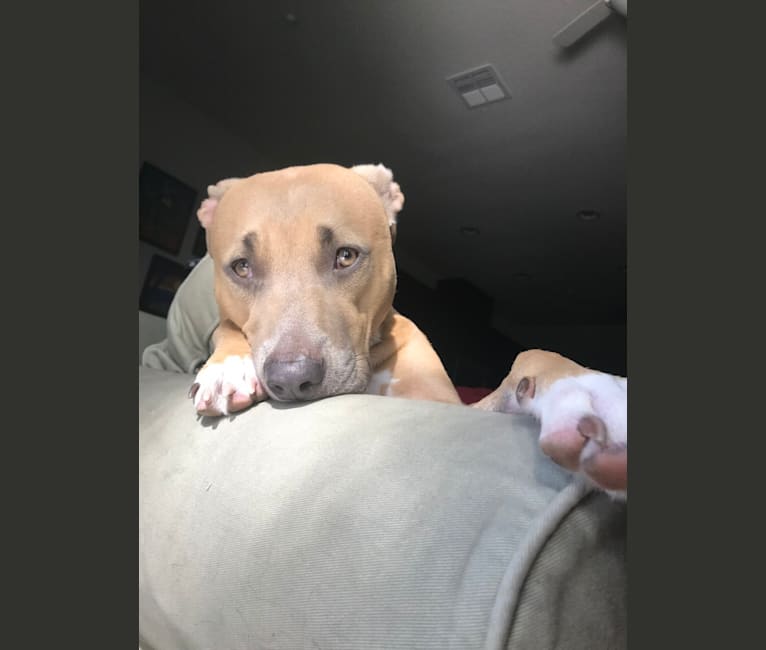
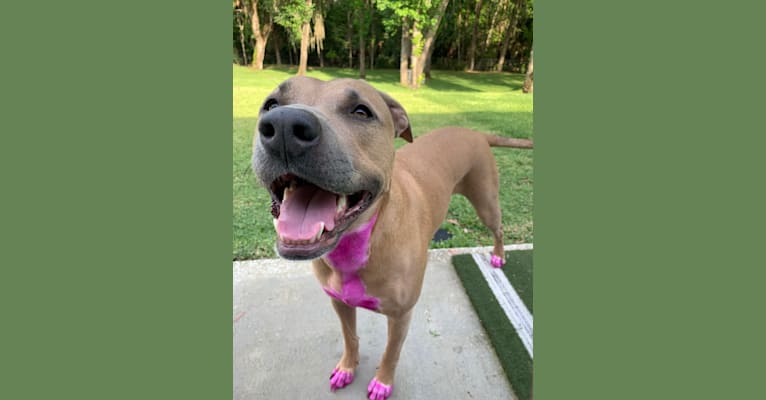
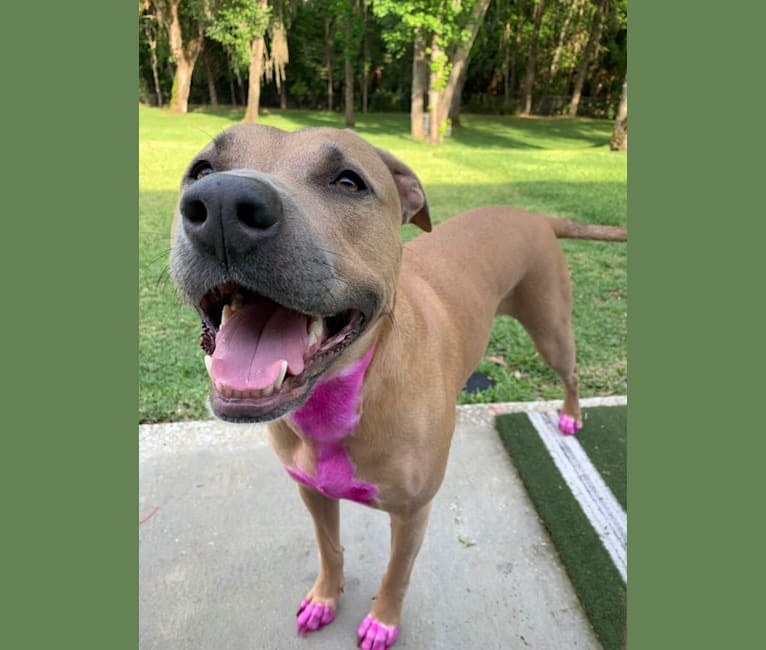
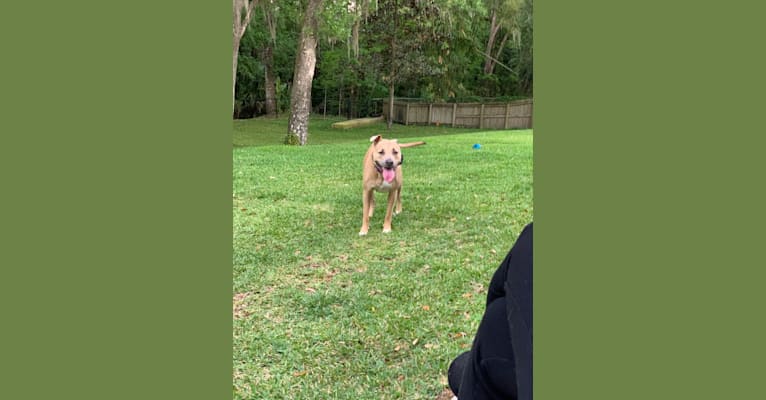
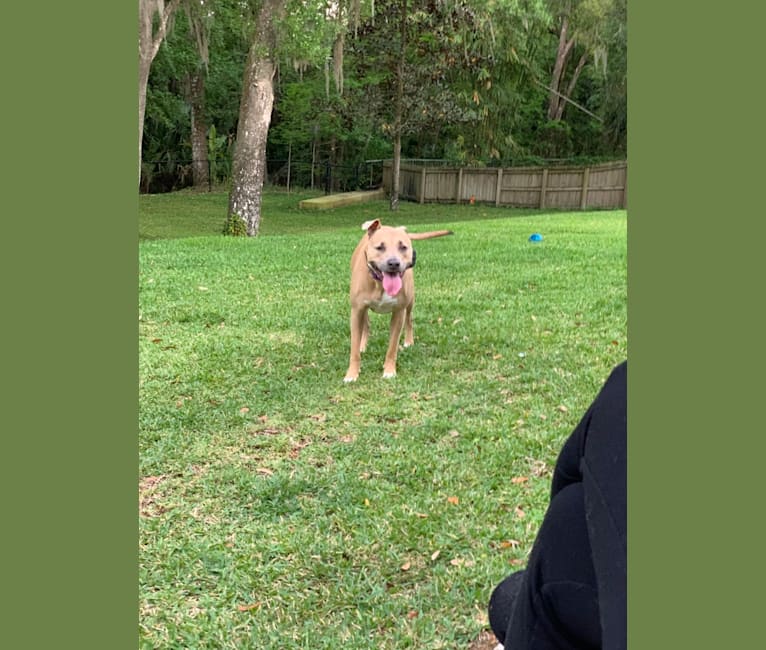
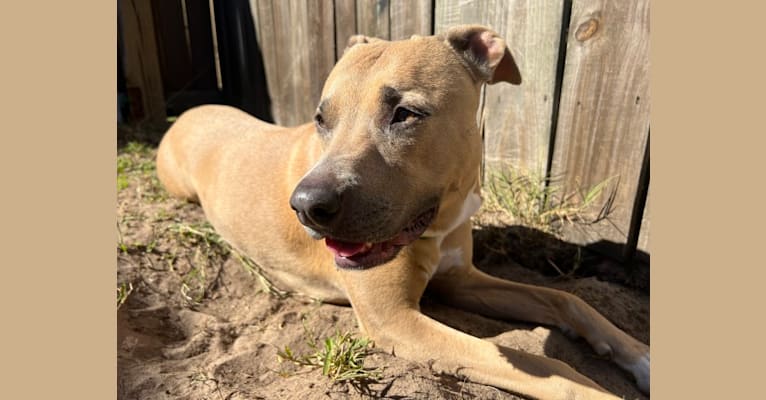
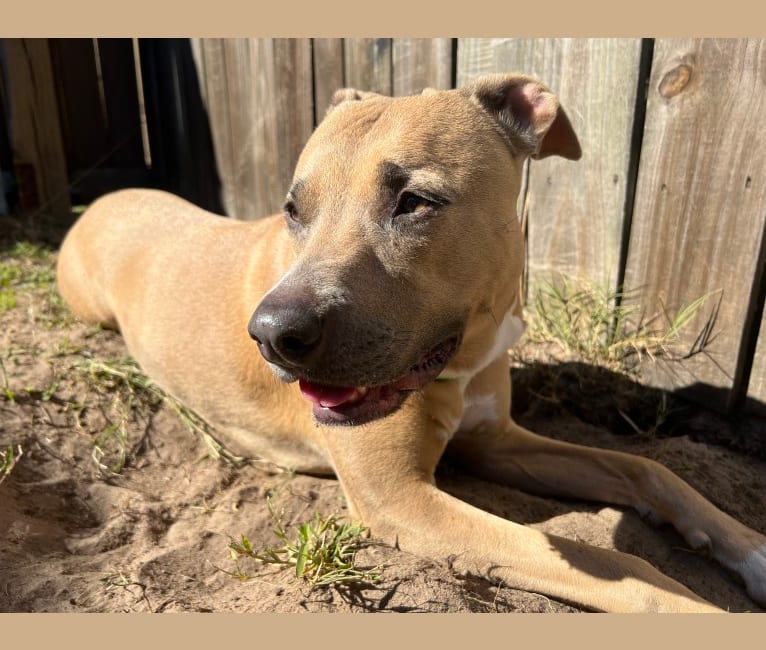
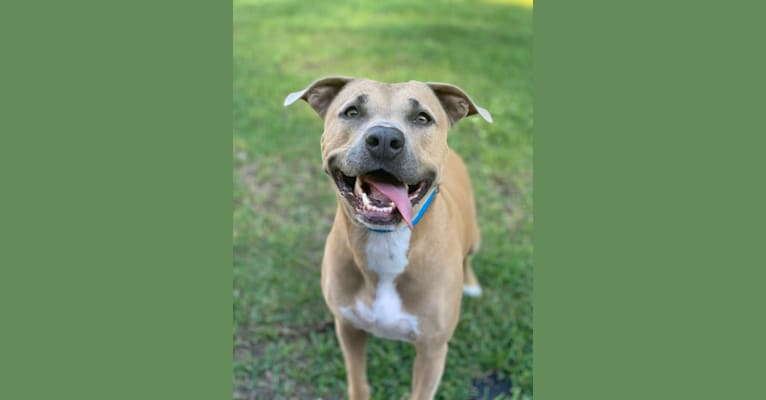
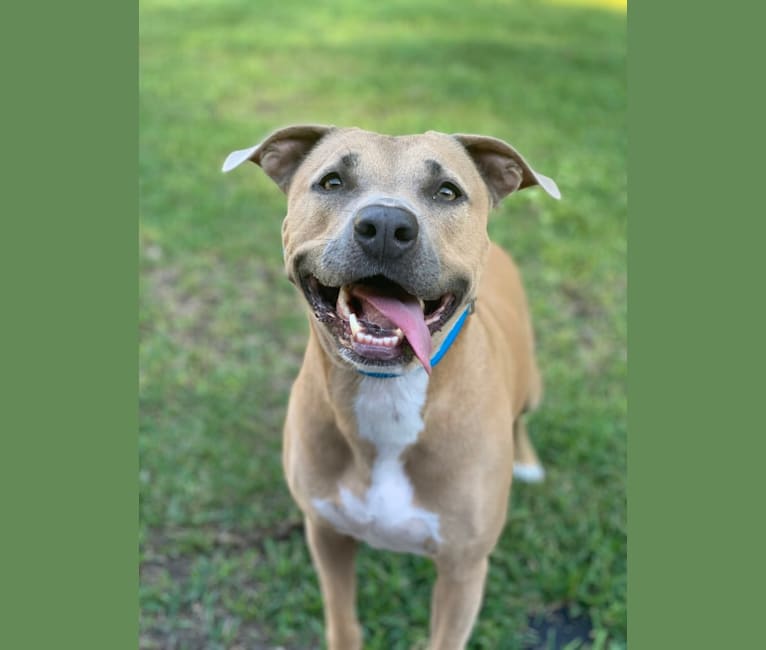
Nina inherited one copy of the variant we tested
No Dogs Available
It looks like you don’t have any dogs on your account yet. Activate a kit now!
Genetic Age
Please note that genetic age is different from calendar age. We can now estimate your dog's calendar age with the Embark Age Test.
The genetic age in this report is an estimation of where your dog is in his or her healthspan. Dogs age at very different rates due to a number of genetic and environmental factors. Body size is a strong genetic influence: for example, a seven year old Great Dane is at the start of his golden years, but a seven year old Pomeranian is just learning what "slow down" means. Just within this example, you can see that the old "one doggie year = seven human years" adage isn’t going to work. And yet, knowing your dog’s age is important: it informs what your dog needs as far as food, frequency of veterinary checkups, and exercise. So how do you best determine how old your dog is?
Embark's genetic age feature calculates how old your dog would be if he or she were aging at an average human rate (using humans in the USA as the baseline). So going back to our Dane/Pom example, we'd estimate a seven year old Great Dane at about 80 years old (senior citizen), but a seven year old Pom would be about 42 (adult). Makes way more sense, right?
| Calendar age | Genetic age |
|---|---|
| 1 year | 17 human years |
| 2 years | 25 human years |
| 3 years | 31 human years |
| 4 years | 38 human years |
| 5 years | 44 human years |
| 6 years | 51 human years |
| 7 years | 57 human years |
| 8 years | 64 human years |
| 9 years | 70 human years |
| 10 years | 77 human years |
| 11 years | 83 human years |
| 12 years | 90 human years |
All we need from you is a calendar age. It's okay if this is an estimation: it is just a starting point. We then factor in your dog's breed composition, information at certain genes that affect size, and their inbreeding coefficient to calculate genetic age. Like in humans, in dogs females tend to live longer than males (so an “80 year old” female dog = 80 year old woman). Exercise and diet also play a role in how long your dog will live. Nevertheless, genetic age is the primary risk factor for numerous diseases in dogs, including cancer, kidney disease, osteoarthritis, cataracts, cardiac disease and cognitive decline. It can help you and your vet know what you should feed your dog, what screenings to get, and other aspects of your dog’s care.
Wolfiness score
How wolfy is my dog?
Most dogs have wolfiness scores of 1% or less. We find populations and breeds with higher scores of 2-4% occasionally, and unique dogs with scores of 5% or above more rarely.
What it means for my dog
Your dog’s Wolfiness Score is not a measure of recent dog-wolf hybridization and does not necessarily indicate that your dog has some recent wolf ancestors. (If your dog has recent wolf ancestors, you will see that in the breed mix report.) Instead, the Wolfiness Score is based on the number of ancient genetic variants your dog has in our unique Wolfiness marker panel. Wolfiness scores up to 10% are almost always due to ancient wolf genes that survived many generations, rather than any recent wolf ancestors. These ancient genes may be a few thousand years old, or may even date back to the original domestication event 15,000 years ago. They are bits of a wild past that survive in your dog!
The science
Your dog’s Wolfiness Score is based on hundreds of markers across the genome where dogs (or almost all of them) are the same, but wolves tend to be different. These markers are thought to be related to "domestication gene sweeps" where early dogs were selected for some trait. Scientists have known about “domestication gene sweeps” for years, but do not yet know why each sweep occurred. By finding rare dogs carrying an ancient variant at a certain marker, we can make associations with behavior, size, metabolism, and development that likely caused these unique signatures of “doggyness” in the genome.
Predicted Adult Weight
How does weight matter?
For people with puppies, you probably want to know how big of a crate to buy or just how big to expect your dog to become. But genetic weight is also useful for people with fully grown dogs. Just like with people, overweight and obese dogs suffer reduced length and quality of life. They can develop chronic health conditions and suffer from limited mobility and other issues. While over half of American dogs are overweight or obese, fewer than 15% of their owners realize it. By comparing your dog’s weight to their genetic predicted weight you have one more piece of information about their ideal weight. With this and other pieces of information like weight history and body condition, you and your veterinarian may want to discuss your dog’s diet, exercise, and weight control plan to give your pup the longest, healthiest life possible.
How do we predict weight?
Our test is the only dog DNA test that provides true genetic size not based just on breed ancestry but based on over a dozen genes known to influence a dog’s weight. It uses the most advanced science to determine your dog’s expected weight based on their sex, the combination of these genes, and breed-specific modifiers.
How accurate is the predicted weight?
Unlike in people, healthy weight in dogs is controlled largely by only a few genes. Our algorithm explains over 85% of the variance in healthy adult weight. However, due to a few as-yet-undiscovered genes and genetic interactions that affect size, this algorithm sometimes misses. Occasionally it misses by a fairly large amount especially when a dog has a breed with an unknown size-influencing gene. If we have missed your dog’s weight, your dog may be a scientific discovery waiting to happen! Please be sure to go to the Research tab and complete the Getting to know your dog survey, where you can answer questions about your dog’s current weight and body shape. This information will inform our ongoing research into the genetics of size and weight in dogs.
Haplotypes
Revealing your dog’s ancient heritage
Haplotypes are particular DNA sequences that are inherited entirely from a dog’s mom (maternal) or dad (paternal).
Because they are inherited whole, your dog and his or her mom share the exact same maternal haplotype. If you have a male dog, your dog and his dad share the exact same paternal haplotype (female dogs don’t inherit paternal haplotypes).
Because most breeds were started with only a few individual dogs, many breeds are dominated by only one or a few haplotypes.
Haplogroups
Revealing your dog’s ancient heritage
Haplogroups are groups of similar DNA sequences (called haplotypes) that are inherited entirely from the mother (maternal) or father (paternal) and don’t get shuffled up like other parts of your dog’s genome.
These groups all originally descend from one male or female wolf, usually one that lived tens of thousands of years ago. Because they are inherited whole and not shuffled like other DNA, they can be used to trace the ancestral routes that dogs took around the globe en route to your home.
Only male dogs have paternal haplogroups because they are determined by the Y chromosome, which only male dogs have. Both males and females have maternal haplogroups, which come from a part of DNA called the mitochondrial DNA.
Breed analysis
Breed analysis is based on comparing your dog’s DNA with the DNA of dogs from over 350 breeds, types and varieties.How are Nina's ancestors represented in her DNA?
All dogs are related and share some DNA. Siblings share lots of their DNA (half of it in fact), cousins share a bit less (an eighth), and so on. Because dog breeds are made up of a closed group of dogs, all dogs in that breed share a lot of their DNA, typically about as much as second cousins, though it varies by breed. Different breeds that are closely related share somewhat less DNA, and dogs from very different breeds share even less DNA (but still much more DNA than either dog shares with a cat).
DNA is inherited in pieces, called chromosomes, that are passed along from parent to offspring. Each generation, these chromosomes are broken up and shuffled a bit in a process known as recombination. So, the length of the segments your dog shares with her ancestors decreases with each generation above her: she shares longer segments with her mom than her grandma, longer segments with her grandma than her great-grandma, and so on.
How does Embark know which breeds are in Nina?
We can use the length of segments Nina shares with our reference dogs to see how many generations it has been since they last shared an ancestor. Long segments of DNA that are identical to known purebred dogs tell Embark's scientists that Nina has, without a doubt, a relative from that breed. By testing over 200,000 genetic markers, we build up her genes one DNA segment at a time, to learn the ancestry with great certainty. Other dog DNA tests look at many fewer genetic markers and have to take a guess at breed ancestry based on that.
What does this mean for Nina's looks and behavior?
Look closely and you'll probably find Nina has some physical and/or behavioral resemblance with her ancestor's breeds. The exact similarity depends on which parts of DNA Nina shares with each breed. Some traits associated with each breed are listed in the Breed & Ancestry section of our website. Embark will tell you even more about Nina's traits soon!
P.S. In a small proportion of cases, we find dogs that don’t share segments with other dogs we have tested, indicating the presence of a rare breed that is not part of our reference panel or possibly a true "village dog" without any purebred relatives at all. In these rare cases we contact the owner to find out more and let them know about their unique dog before they get their results. With this in-depth detective work, we are pushing science forward by identifying genetically unique groups of dogs.
Still have questions?
Let us know with our contact form.
What are “Dogs Like Nina?”
“Dogs Like Nina” are based on the percentage of breeds the two dogs have in common. For example, two dogs that are both 27% Golden Retriever and 73% Poodle will have a score of 100%. Sometimes dogs with high scores look alike, and sometimes they don’t — either way the comparison is based on each dog’s unique DNA.
“She’s very curious and gets in everyone’s business (“Nosey Nina”). She sometimes watches TV and enjoys FaceTiming family. She has developed an obsession with chasing squirrels and lizards and loves sleeping under the covers.”
Place of Birth
Florida, USA
Current Location
Winter Park, Florida, USA
From
Auburndale, Florida, USA
This dog has been viewed and been given 13 wags
Genetic Breed Result
American Bully
The American Bully may look intimidating with its muscular build, but these dogs are bred to be the ideal family or companion dog. This breed is notable for coming in several different size and type varieties, so there's a lot of diversity in their appearance. They're a newer breed, originating in the 80s and 90s in the United States.
Learn More
American Pit Bull Terrier
The American Pit Bull Terrier originated in the British Isles and descends from the Mastiff-type dogs introduced to England in antiquity. The breed was brought over to the United States by English immigrants in the 1800s, and quickly became one of the most popular and widespread breeds there.
Learn More
American Staffordshire Terrier
American Staffordshire Terriers are powerful but playful dogs that are both loyal and affectionate with their owners.
Learn More
Start a conversation! Message this dog’s humans.
Dogs Like Nina

Discover dogs who share a similar breed mix to Nina. A higher score means the two dogs have more of their breed mix in common. A score of 100% means they share the exact same breed mix!
Click or tap on a pic to learn more about each dog and see an in-depth comparison of their DNA, breeds, and more.
Building blocks of life
See which breed every part of Nina’s DNA comes from!
Genes from your dog’s breeds serve as the building blocks to creating your unique pooch
Dogs have 39 pairs of chromosomes, almost double humans who have 23. 38 of those pairs are the same for all dogs while the 39th is the sex chromosomes - two X’s for females and one X and one Y for males. One copy of each chromosome came from your dog’s mother and one from your dog’s father. Each copy contains between 24 million and 123 million bases, or letters of DNA code, for 2.5 billion total letters inherited from each parent. This chromosome illustration shows a representation of each of your dog’s 38 pairs of chromosomes (excluding the X and Y sex chromosomes).
Because the members of a breed have similar stretches of DNA, we can use our 200,000+ genetic markers to determine what part of each chromosome in your dog came from what breed. For each pair of chromosomes, your dog’s mom and dad each gave your dog one copy of that chromosome, for a grand total of 78 chromosomes. So if your dog’s mom was a poodle and dad was a schnauzer then the painting would show one complete poodle and one complete schnauzer chromosome for each pair. The more complex your dog’s ancestry, the more complex the painting, as in each generation recombination (the splitting apart and "shuffling around" of genes between paired chromosomes) mixes up bits of chromosome from grandparents, great-grandparents, and beyond.
Each trait your dog exhibits, such as fur shedding, is based on the letter at one or more locations in your dog’s genome. For example the location determining if your dog sheds their fur is located on chromosome 1. Some other traits, like size, are complexly inherited from many locations, including ones on chromosomes 1, 3, 4, 7, 10, 15, and more. Your dog looks the way it does not because of averaging or blending the breeds that form it, but because specific traits were inherited from specific breeds. That’s one reason your mix may look, act, and have certain health issues much more like one breed than another!
DNA Breed Origins
Explore
Changes to this dog’s profile
- On 6/4/2019 changed handle from "nina52" to "noseynina"
Our policy is that each dog’s profile should accurately portray the dog to which the genetic reports belong.
To help ensure adherence to this policy, we show here any changes that have been made to the name or handle (web address) of this dog.
If you believe that this profile is in violation of this policy, you may contact us to report it.
Health Summary
Nina inherited two variants that you should learn more about.
Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis, Cerebellar Ataxia, NCL4A
What does this result mean?
This variant should not impact Nina’s health. This variant is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning that a dog needs two copies of the variant to show signs of this condition. Nina is unlikely to develop this condition due to this variant because she only has one copy of the variant.
What is Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis, Cerebellar Ataxia, NCL4A?
A lysosome is a structure within the cell that digests and removes waste. When the lysosome cannot recycle waste properly, the waste accumulates and causes the cell to die. This form of lysosomal storage disease causes adult onset neurologic signs.
Progressive Retinal Atrophy, crd4/cord1
Nina inherited one copy of the variant we tested
What does this result mean?
This variant should not impact Nina’s health. This variant is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning that a dog needs two copies of the variant to show signs of this condition. Nina is unlikely to develop this condition due to this variant because she only has one copy of the variant.
What is Progressive Retinal Atrophy, crd4/cord1?
PRA-CRD4/cord1 is a retinal disease that causes progressive, non-painful vision loss over a 1-2 year period. The retina contains cells, called photoreceptors, that collect information about light and send signals to the brain. There are two types of photoreceptors: rods, for night vision and movement, and cones, for day vision and color. This type of PRA leads to early loss of cone cells, causing day blindness before night blindness.
Breed-Relevant Genetic Conditions
Progressive Retinal Atrophy, crd1
Identified in American Bullies, American Pit Bull Terriers, and more
Variant not detected
Progressive Retinal Atrophy, crd2
Identified in American Bullies, American Pit Bull Terriers, and more
Variant not detected
Canine Multifocal Retinopathy, cmr1
Identified in American Bullies
Variant not detected
Urate Kidney & Bladder Stones
Identified in American Bullies, American Pit Bull Terriers, and more
Variant not detected
Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis 10, NCL 10
Identified in American Bullies
Variant not detected
L-2-Hydroxyglutaricaciduria, L2HGA
Identified in American Bullies, American Pit Bull Terriers, and more
Variant not detected
Ichthyosis
Identified in American Bullies
Variant not detected
Additional Genetic Conditions
Explore
What is a linkage test?
DNA sequences that are close together on a chromosome tend to be inherited together. Because of this, we can use genetic variation surrounding a specific variant (i.e. "linked" to it) to infer the presence or absence of a variant that is associated with a health condition or trait.
Linkage tests are not as predictive of your dog’s true genotype as direct assays, which we use on most other genetic conditions we test for.
Traits
Explore the genetics behind your dog’s appearance and size.
No Result
For every test, we run multiple assays to ensure the accuracy of the results we deliver. For your dog, one or more of these produced inconclusive or low confident results. Therefore, we are not able to provide you with a result at this time.
Base Coat Color
No Result
For every test, we run multiple assays to ensure the accuracy of the results we deliver. For your dog, one or more of these produced inconclusive or low confident results. Therefore, we are not able to provide you with a result at this time.
Coat Color Modifiers
No Result
For every test, we run multiple assays to ensure the accuracy of the results we deliver. For your dog, one or more of these produced inconclusive or low confident results. Therefore, we are not able to provide you with a result at this time.
Other Coat Traits
No Result
For every test, we run multiple assays to ensure the accuracy of the results we deliver. For your dog, one or more of these produced inconclusive or low confident results. Therefore, we are not able to provide you with a result at this time.
Other Body Features
No Result
For every test, we run multiple assays to ensure the accuracy of the results we deliver. For your dog, one or more of these produced inconclusive or low confident results. Therefore, we are not able to provide you with a result at this time.
Body Size
No Result
For every test, we run multiple assays to ensure the accuracy of the results we deliver. For your dog, one or more of these produced inconclusive or low confident results. Therefore, we are not able to provide you with a result at this time.
Performance
Explore
Through Nina’s mitochondrial DNA we can trace her mother’s ancestry back to where dogs and people first became friends. This map helps you visualize the routes that her ancestors took to your home. Their story is described below the map.
A1e
A2a

A1e
This female lineage likely stems from some of the original Central Asian wolves that were domesticated into modern dogs starting about 15,000 years ago. It seemed to be a fairly rare dog line for most of dog history until the past 300 years, when the lineage seemed to “explode” out and spread quickly. What really separates this group from the pack is its presence in Alaskan village dogs and Samoyeds. It is possible that this was an indigenous lineage brought to the Americas from Siberia when people were first starting to make that trip themselves! We see this lineage pop up in overwhelming numbers of Irish Wolfhounds, and it also occurs frequently in popular large breeds like Bernese Mountain Dogs, Saint Bernards and Great Danes. Shetland Sheepdogs are also common members of this maternal line, and we see it a lot in Boxers, too. Though it may be all mixed up with European dogs thanks to recent breeding events, its origins in the Americas makes it a very exciting lineage for sure!
A2a
Part of the large A1e haplogroup, we see this haplotype in village dogs up and down the Americas as well as French Polynesia. Among the breed dogs we have detected it in, we see it most frequently in English Springer Spaniels, Papillons, and Collies.

Irish Wolfhounds are a consistent carrier of A1e.
Explore
The Paternal Haplotype reveals a dog’s deep ancestral lineage, stretching back thousands of years to the original domestication of dogs.
Are you looking for information on the breeds that Nina inherited from her mom and dad? Check out her breed breakdown and family tree.
Paternal Haplotype is determined by looking at a dog’s Y-chromosome—but not all dogs have Y-chromosomes!
Why can’t we show Paternal Haplotype results for female dogs?
All dogs have two sex chromosomes. Female dogs have two X-chromosomes (XX) and male dogs have one X-chromosome and one Y-chromosome (XY). When having offspring, female (XX) dogs always pass an X-chromosome to their puppy. Male (XY) dogs can pass either an X or a Y-chromosome—if the puppy receives an X-chromosome from its father then it will be a female (XX) puppy and if it receives a Y-chromosome then it will be a male (XY) puppy.
As you can see, Y-chromosomes are passed down from a male dog only to its male offspring.
Since Nina is a female (XX) dog, she has no Y-chromosome for us to analyze and determine a paternal haplotype.